 SNOW HYDROLOGY (GEOG 4321): SNOW METAMORPHISM
SNOW HYDROLOGY (GEOG 4321): SNOW METAMORPHISM
Instuctor: Mark Williams
Telephone: 492-4794 or 492-8830
Readings
- Avalanche Handbook, pp 45-60.
- Colbeck, Thermodynamics of Snow Metamorphism,
J Glaciology, 1980.
- Physics of Skiing, Appendix.
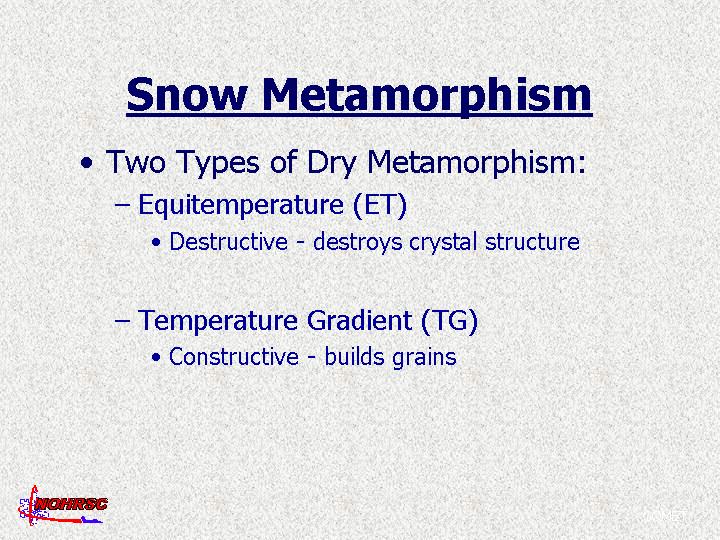
Overview
Initial Changes in New Snow
Equitemperature Metamorphism
Temperature Gradient Metamorphism
Definition
- term borrowed from geology, with same meaning;
- crystalline changes that take place due to the effects
of temperature and pressure
Why of Interest
Causes changes in snow properties, including:
- sintering
- structural strength of snowpack
- permeability of snowpack
- reflectivity of the snow surface
- thermal conductivity of the snowpack
- snow density
These changes in snow properties affect:
- avalanche stability
- avalanche release
- melt-water runoff
- radiant-energy penetration into the snowpack
- release of solutes from the snowpack
Why Snow Metamorphsim Occurs
- Crystalline solid close to its melting temperature
- Thermodynamically unstable
- large surface area to volume ratio
- results in high surface free energy
- thermodynamic equilibrium occurs when
surface to volume ratio is minimized, eg a sphere
or rounded grain.
Examples
Snow crystals begin to change form immediately because
(Avalanche Handbook, pages 46-48):
- Less supersaturation in snowpack than atmosphere
- Large surface to volume ratio: eg stellars
- Therefore high surface free energy
- Thermodynamically unstable
- Snow crystals with the highest surface to volume ratios
(eg dendrites) are the most unstable and change form
most quickly.
- Radius of curvature effects can be very large because
of branched form of many new snow crystals.
- As branches disappear, there is a general DECREASE
in the average particle size.
- However, after the branches disappear, size begins
to increase.
- Larger particles grow at the expense of smaller particles
because
- Sublimation is more efficient from small particles
because of the higher radius of curvature and hence
higher vapor pressure, and
- Water vapor then moves efficiently away from smaller
particles and towards larger particles, which have lower
vapor pressures because of smaller radius of curvature
pressure effects.
- Condensation or redeposition is more efficient
over larger particles because of lower vapor pressures.
- Thus, in a snowpack with a mixture of particle
sizes, the average particle size INCREASES over time,
after the initial decrease in size of particles with
high surface to volume ratios.
Definition
Rounded grains that bond together into simple chains.
Synonyms
- Destructive metamorphism.
- Equitemperature metamorphism.
- Equilibrium metamorphism.
- Radius-dependent metamorphism.
- Radius of curvature metamorphism.

Parameters
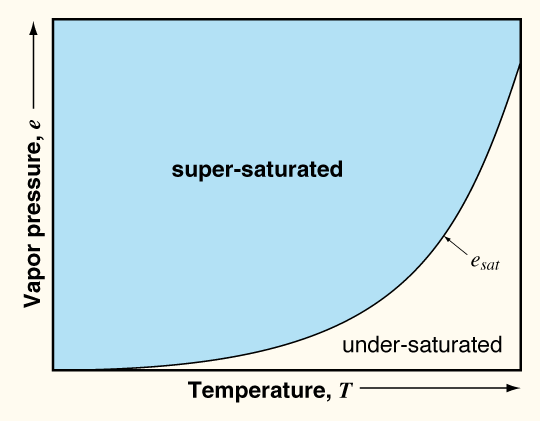
- Temperature gradient in snowpack is less than
10 deg C per meter.
- Vapor diffusion direction governed by radius of curvature
of snow grains, such that there is a loss of mass
from points on individual snow grains (convexities)
and gain in mass in hollows (concavities).
Process
- Saturation vapor pressure is greater over points
and lowest at hollows.
- The reason is that, at saturation, more vapor pressure can be
supported over a convex surface than a flat surface,
and more water vapor can be supported over a flat
surface than a concave surface.
- For a given temperature, the saturation vapor pressure
is greater over a point (convexity) than over a
hollow (concavity).
- Water vapor then moves from a region of high vapor
density (points) to a region of low vapor density
(hollows).
- As water moves away from a point towards a hollow,
the air in the pore space above the point becomes
undersaturated (RH < 100%).
Water then sublimes from the point into the air,
causing a mass loss from the point.
The water vapor above the point again reaches saturation,
then moves towards lower vapor density above hollows.
A positive feedback loop is then setup, such that ice
constantly sublimes to water vapor above points, and
the water vapor moves to areas with lower vapor density,
such as hollows.
- At hollows, the vapor density becomes supersaturated
because of the contribution of water vapor from points.
Water vapor is then deposited into hollows as ice,
filling the hollows.
As water vapor is deposited in hollows, the vapor
density decreases, increasing the vapor density
gradient and causing more water vapor to move from
points to hollows, increasing the amount of
supersaturation.
Another positive feedback loop is established,
causing increased deposition of ice from the vapor
phase to hollows.
- We have established a positive feedback loop,
such that there is a loss of mass from points to
the vapor phase, movement of water vapor to areas
of lower vapor density over hollows, and
deposition of water vapor to ice in the hollows.
- Sintering or bonding of two snow grains occurs by
this process, because whenever two round shapes touch,
a hollow or concavity is formed.
Additional information from Professor Paul Brooks' at the
University of Arizona (former student in this class)
here .
Results
- Reduction in the surface to volume ratio
of snow grains.
- Reduction in surface free energy of snow grains.
- Snow grains fill the pore space in the snowpack.
- Density of the snowpack increases.
- Rounding of snow grains occurs.
- Bonding or sintering of snow grains occurs.
- The strength of the snowpack increases.
- The rate of ET metamorphism increases with increasing
temperature.
Definition
Angular grains with poor sintering
Synonyms:
- constructive metamorphism
- temperature-gradient metamorphism
- kinetic growth
- depth hoar
- sugar snow
Parameters:
- Coupled, simultaneous heat and mass transfer
- temperature gradient > 10 degrees C
- snow density < 350 kg/m^3
- radius of curvature effects not important
Process
TG snow grows by the movement of water vapor
from areas of higher vapor density to areas of lower vapor density,
when there is a vapor density gradient across the pore spaces
that is longer than the vapor density between points and hollows
that drives ET metamorphism.
Generally this occurs from warm areas of the snowpack
(higher temperature results in higher SVP, which results in higher vapor density
at RH = 100%)
to colder areas (lower SVP, thus lower vapor density at RH = 100%),
as the figure below illustrates.
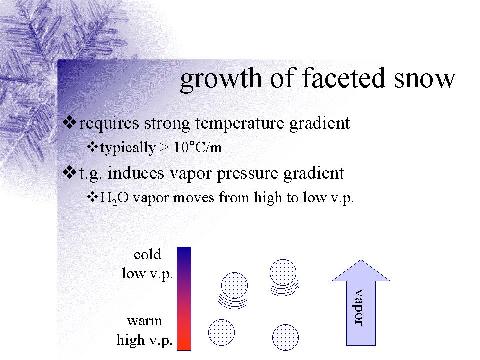
- Strong temperature gradient
over a short distance (10 0 C m -1 )
- Causes a strong vapor pressure or vapor density gradient
- Water vapor then moves from the area of high water vapor
density (warmer area of snowpack) to lower water
vapor density (colder area of snowpack).
- Supersaturation becomes relatively high as the
water vapor moves into a colder region of the snowpack,
which has a lower saturation vapor pressure because of
colder temperatures.
- This relatively large amount of supersaturation
results in immediate deposition whenever the supersaturated
air contacts a nucleating surface.
- This deposition occurs before water vapor can move
from convexities of concavities.
- Generally, deposition occurs as
facets in a plane.
- These facets can be from one molecule to several
thousand molecules thick.
- The angle of deposition is approximately 120
O, leading to a stepped,
then scrolled, and finally cup-shaped appearance.
- The cup grows TOWARDS the water vapor source,
or TOWARDS the warm part of the snowpack.
- Here's some examples:
- Hence, the hollow part of TG snow grains is open
towards the water vapor source, and
- TG snow grains become larger away from their initial
point of origin and towards the water vapor source.
- The relocation of mass caused by temperature gradients
in snow is usually on the scale of individual snow grains,
eg a hand-to-hand process.
Results
- Density remains relatively constant,
usually less than 350 kg/m3.
- Necks between snow grains remain the same size.
- Crystal size is usually greater than 3 millimeters.
- Decrease in the structural strength of the snowpack.
- TG grains grow towards the vapor source.
- Grains are usually vertically oriented.
- The vertical orientation resists compaction by gravity,
further resisting an increase in density.
- The large, vertical snow grains act as levers
with little attachment or bonding to neighboring snow
grains.
- Mechanical strength is thus low.
- Almost always forms a weak layer in the snowpack.
- Forms at the bottom of the snowpack,
on the underside of ice lenses, and
near rocks and trees.
SUMMARY
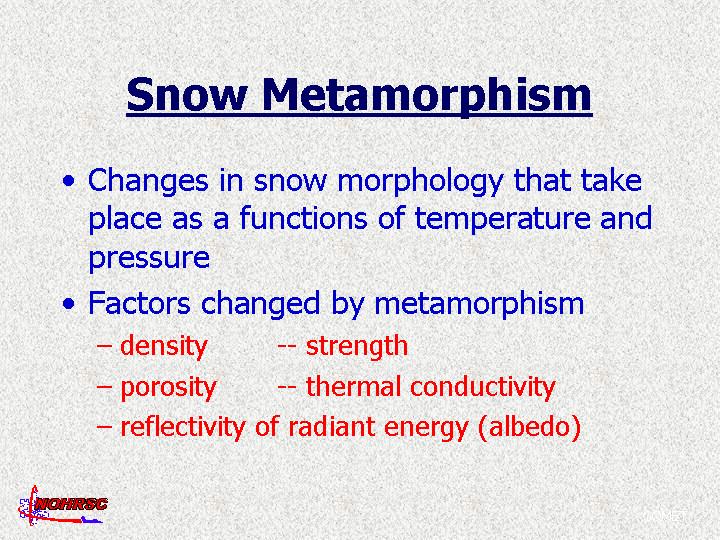






 SNOW HYDROLOGY (GEOG 4321): SNOW METAMORPHISM
SNOW HYDROLOGY (GEOG 4321): SNOW METAMORPHISM  SNOW HYDROLOGY (GEOG 4321): SNOW METAMORPHISM
SNOW HYDROLOGY (GEOG 4321): SNOW METAMORPHISM
